AC Power Consumption Formula: Manual Calculation Explained
AC Power Consumption Formula: Manual Calculation Explained
Air conditioners (ACs) are one of the major contributors to electricity consumption in offices and residential premises. By determining how much electricity your AC uses and how to calculate your electricity bill manually, you can save money and manage your electricity consumption better. So, in this guide below, we will tell you how to calculate AC electricity consumption using simple math and real-life examples and how to calculate AC bills manually.
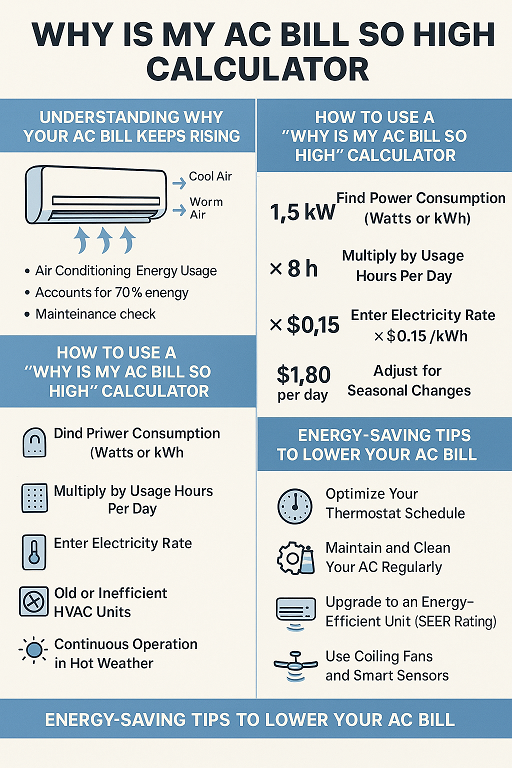
Understanding AC Power Consumption
Air conditioners use electricity to cool your home. This also depends on the capacity of the AC, which is measured in tons or watts, and how long it can run before it needs to be recharged. It is important to know the difference between watts and kilowatt-hours (kWh) because energy bills are calculated in terms of the ratio of energy used to the amount of time measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
What is Wattage and Kilowatt-hour (kWh)?
- Watt (W): It is the measure of the power at any moment. Incidentally, a 1 Ton AC may have a power potential of approximately 1, 200 watts.
- Kilowatt-hour (kWh): This is a way to measure overall energy used. 1kWh is about using 1000 watts nonstop for 1 hour. Electricity charging is done in terms of air conditioner.
Knowing what these units are also helps you determine how much power your AC uses.
How to Convert Watts to Kilowatt-hours (kWh)
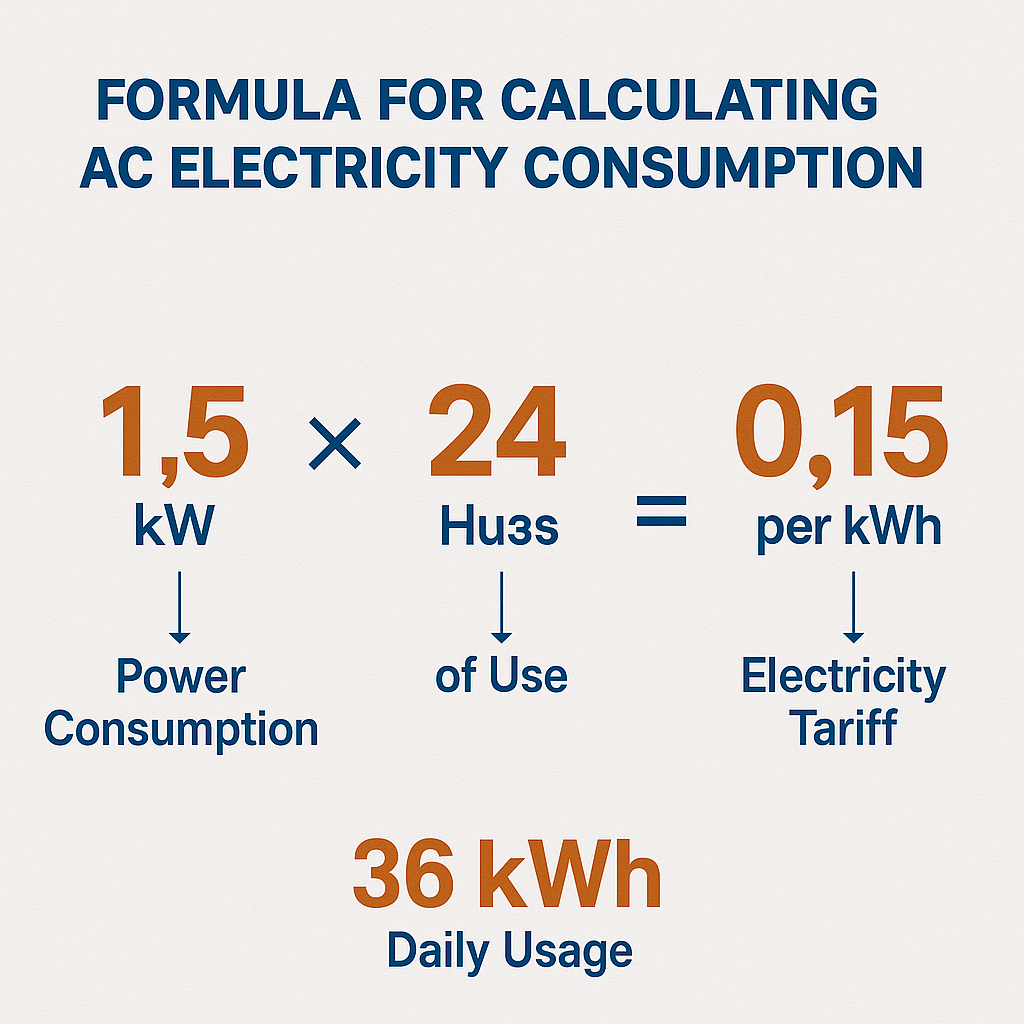
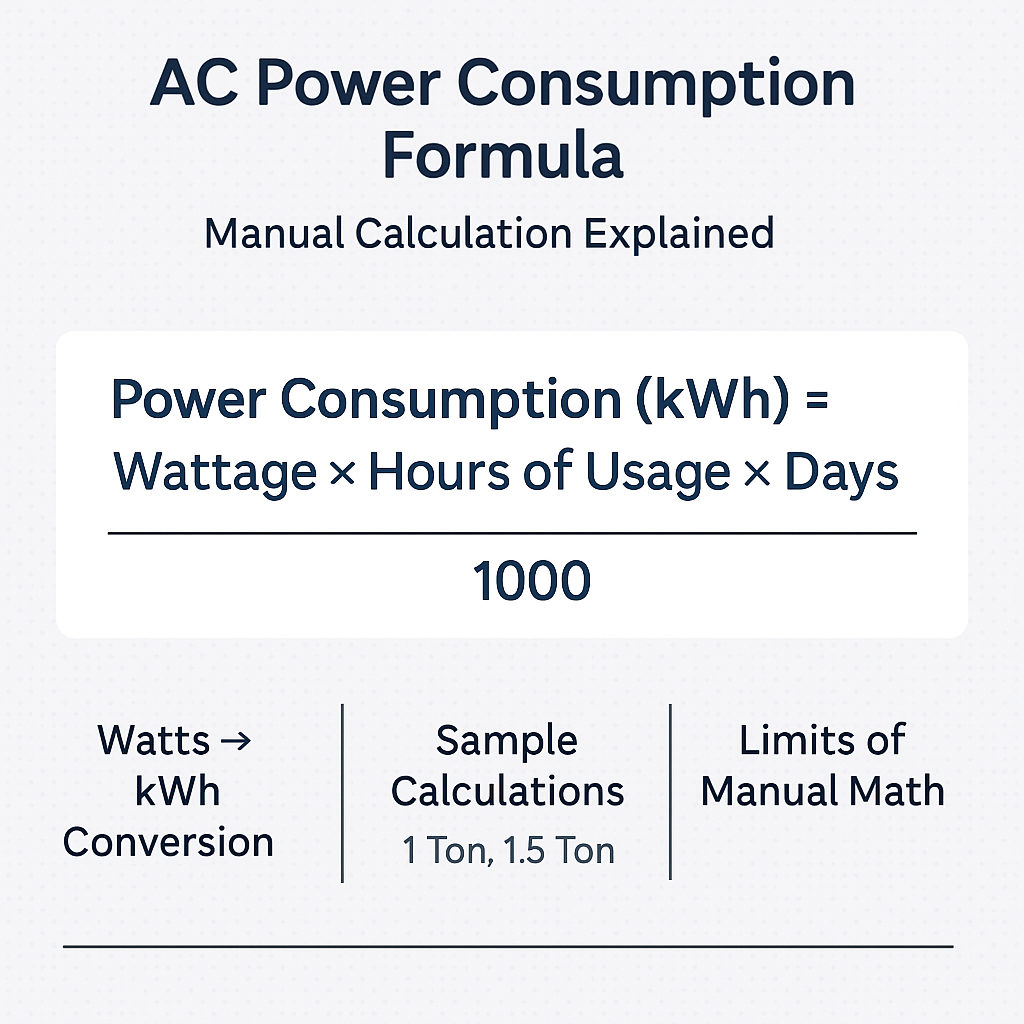
In order to determine the amount of energy that your AC consumes, you first have to convert wattages to kWh. The general Formula is
Energy (kWh)=1000Power (Watts)×Time (hours)
This equation is an equation whereby you take the power rating of the AC and multiply it by the running hours and divide by 1,000 to find out the watts to kilowatts.
Formula for AC Power Consumption
If the power rating of your AC is p, watts and it works for𝑡, the energy in kWh is given as:
AC Power Consumption=1000/P×t
Where:
- P = Power rating in watts
- t = Time in hours
This basic formula is the backbone of manually calculating AC power consumption.
Sample Calculations for AC Units
The formula will be applied in real life examples of the commonly used AC sizes.
Calculating Power Consumption for 1 Ton AC
A commonly exchanged 1 Ton AC sucks up about 1200 watts. If you run it for 8 hour day:
Energy=1000/1200×8=9.6 kWh/day
Electricity price is $0.12 kWh and the daily cost is:
9.6×0.12=1.15 USD/day
Calculating Power Consumption for 1.5 Ton AC
An air conditioner of 1.5 Ton will consume something close to 1,800 watts. The eight-hour run
Energy= 1000/1800×8 =14.4 kWh/day
Daily cost at $0.12 per kWh:
14.4×0.12=1.73 USD/day
How to Calculate Your AC Electricity Bill Manually
After knowing the rate at which your AC was using energy per day in kWh units, the product of that rate with the electricity rate/ charge on your utility bill will be what you pay per year. Again, multiply by the number of days in the billing period to calculate how much your AC bill will be.
Take the case of a 1 Ton AC used 8 hours per day in 30 days:
9.6×30×0.12=34.56 USD/month
Factors Affecting Your AC Power Consumption
- Time of usage: The longer the usage is the more power is consumed.
- Older units: consume more power.
- Most power: Greater tonnage gives you greater watts.
- Ambient temperature: Higher temperatures make a day hotter resulting in more usage.
Limitations of Manual AC Power Consumption Calculation
Although this manual formula may be easy to understand, it does not take into account all the real-life aspects that influence energy consumption.
Role of Power Factor and Other Electrical Variables
- Power Factor (PF): It represents the discrepancy between the two consumptions of power. A low PF indicates that your AC could be using more power than the rated power supply has.
- Voltage swings: The voltage variations burn up energy.
- Compressor cycles: AC compressors do not operate this entire time; they go on/off, and this affects the real power consumption.
This implies that, the amount of electricity which you actually pay might not be the same as manual calculations.
Tips to Reduce AC Power Consumption
- Install energy efficient air conditioners (that have high EER or stars).
- Maintain an air conditioner regularly to work perfectly.
- Make use timer programs for maintaining a limit on usage.
- Make sure that your room is sealed off properly in order to prevent the entry of cold air.
- Be sure to set up the temperature at a suitable level (e.g. 24-26°C).
These can cut down your AC power bills a lot.
The Most Frequently Asked Questions concerning AC Power Consumption and Billing
1. What is the error in whose focus do you think the manual AC power consumption formula can be deviated?
Answer: It provides good estimate which can be varied because of compressor cycles and due to power factor.
2. Does power consumption depend on conversations to be carried on the AC size?
Answer:The higher the tonnage unit is the more power is used.
3. Is it possible to apply this formula to other appliances?
Answer:So, it would be applicable to any appliance we know its wattage.
4. What is a power factor and why it is essential?
Answer: Power factor indicates the efficiency in use of electrical power; low power factor will add cost to power.
5. What are the implications of energy star ratings on the AC consumption?
Answer:The more stars the more efficient and the less consumed.
6. Is it possible that Sophia to pay more because of the voltage fluctuations?
Answer: Yes, unstable electricity can lead to increased consumption of energy and energy bills
.